Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): What It Is and How to Manage It
If you or someone you know has taken a hard blow to the head, chances are you’ve heard the term “traumatic brain injury.” A TBI isn’t just a scary phrase – it’s a real medical condition that can range from a mild concussion to serious brain damage. Knowing the basics helps you act fast and support recovery.
Common Signs & When to Seek Help
Symptoms show up right after the injury or may develop over hours or days. Look for any of these:
- Headache that won’t go away
- Dizziness, balance problems, or trouble walking
- Confusion, memory gaps, or feeling “out of it”
- Nausea or vomiting (especially if repeated)
- Vision changes, double‑vision, or light sensitivity
- Slurred speech or difficulty finding words
- Unusual sleepiness or trouble staying awake
If you notice any of these, especially vomiting, worsening headache, seizures, or loss of consciousness, call emergency services immediately. Even a mild concussion deserves professional assessment – hidden bleeding can become dangerous fast.
Steps for Recovery and Ongoing Care
The first 24‑48 hours are crucial. Follow the doctor’s orders: rest, limit screen time, and avoid alcohol or drugs that could worsen brain swelling. Physical and cognitive rest means no heavy lifting, intense exercise, or multitasking on computers.
After the initial phase, gradual re‑introduction of activity helps rebuild strength. Start with short walks, gentle stretching, and simple mental tasks like puzzles. Track how you feel – if symptoms flare up, pull back a bit.
Nutrition also plays a role. Hydrate well and eat foods rich in omega‑3 fatty acids (fish, walnuts) and antioxidants (berries, leafy greens). These support brain repair and reduce inflammation.
Sleep is non‑negotiable. Aim for 7–9 hours of uninterrupted rest each night. A consistent sleep schedule can ease headaches and improve memory.
Physical therapy or occupational therapy may be recommended if balance, coordination, or daily tasks are affected. Therapists teach exercises that target the specific brain regions impacted by the injury.
Keep a symptom journal. Note when you feel better or worse, what activities you were doing, and any new issues. This record helps your healthcare team adjust treatment plans.
Finally, don’t ignore emotional health. Mood swings, anxiety, or depression are common after TBI. Talking to a counselor, joining a support group, or using mindfulness apps can make a big difference.
Our site has dozens of articles that dive deeper into medication safety, pain management, and lifestyle tips – all useful for anyone navigating a brain injury. Bookmark the tag page and explore topics like safe online pharmacy purchases, supplement guides, and recovery‑focused advice.
Recovering from a traumatic brain injury takes time, patience, and the right information. By spotting warning signs early, following medical advice, and embracing gradual rehab, you give your brain the best chance to heal.
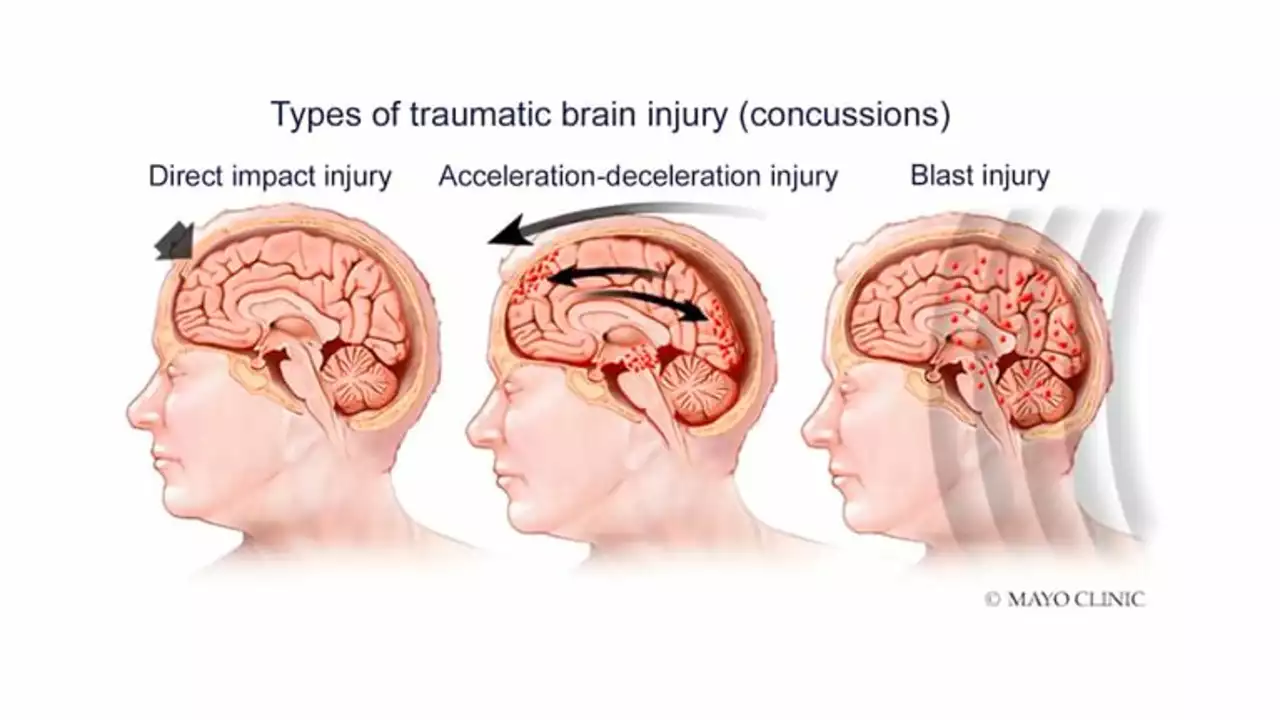
After delving into some medical research, I've discovered that tranexamic acid plays a significant role in treating traumatic brain injuries. It's a powerful drug that helps curb bleeding by inhibiting enzymes that dissolve blood clots. As a result, it can reduce the chance of a hemorrhage and potentially save lives. However, it's crucial to administer this medication within a few hours of injury for maximum effectiveness. Despite its benefits, like all medicines, it's important to be aware of potential side effects and discuss them with a healthcare provider.
Read More