Understanding Tranexamic Acid and its Mechanism
As a blogger and a health enthusiast, I find it essential to explain medical jargon to make it more understandable to everyone. One of the terms that caught my attention recently is "tranexamic acid." Some of you might have heard of it, while others might find it completely unfamiliar. So, what is tranexamic acid? Simply put, tranexamic acid (TXA) is a medication that helps prevent excessive bleeding by promoting clot formation. It's like a superhero that stops the bad guys—in this case, the bad guys being excessive bleeding. The mechanism of action of TXA is quite fascinating. It works by inhibiting the enzymes that dissolve blood clots. In other words, it helps to stabilize the clot formation at the site of injury, reducing the risk of heavy bleeding.
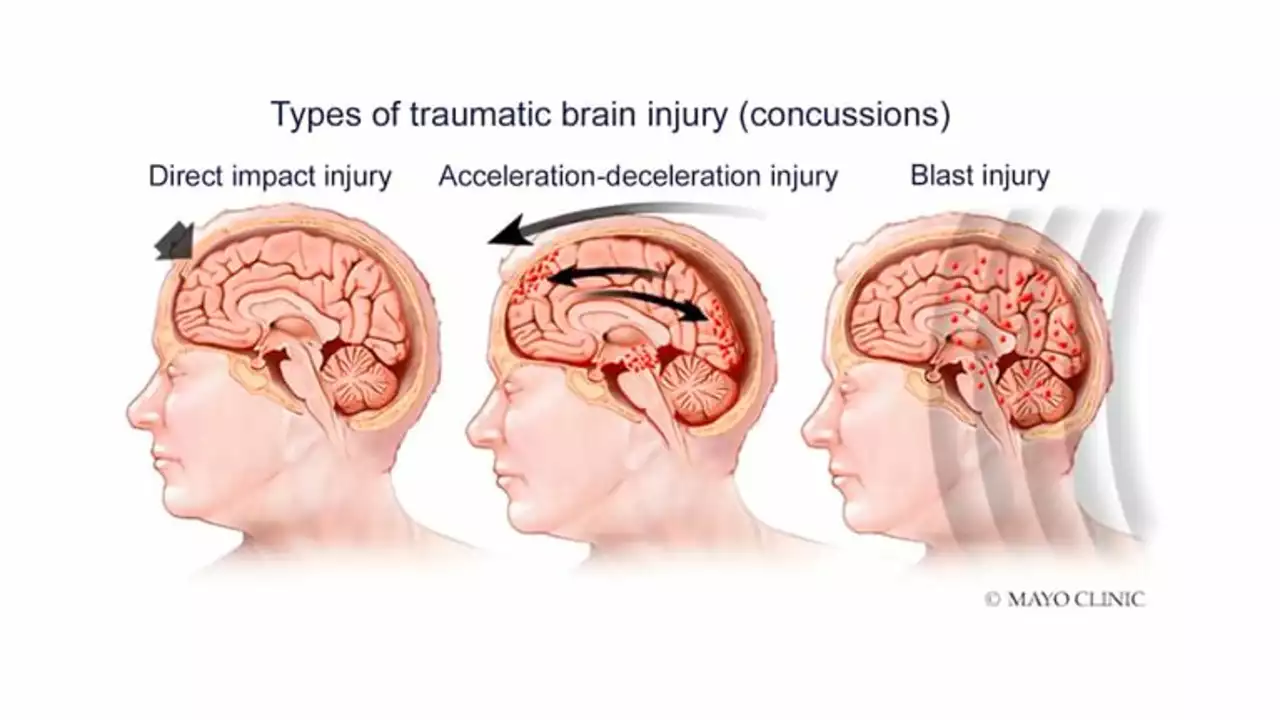
The Role of Tranexamic Acid in Traumatic Brain Injury
Now that you know what tranexamic acid is and how it works, let's dive into its role in traumatic brain injury (TBI). Traumatic brain injury is a significant cause of death and disability worldwide. The primary concern with TBI is the potential for heavy bleeding in the brain, which can lead to serious complications, including death. This is where TXA comes into the picture. By helping to stabilize clot formation, TXA helps to stop the bleeding in the brain and reduce the risk of death and serious complications. Numerous studies have shown that early administration of TXA can significantly improve outcomes in patients with TBI.
Supporting Studies on the Efficacy of Tranexamic Acid
It's always prudent to back up statements with evidence, and in this case, I want to share some of the research studies that support the use of TXA in TBI. One of the most notable is the CRASH-3 trial which involved over 12,000 patients from 29 countries. This study showed a significant reduction in death due to bleeding in the brain when TXA was administered within three hours of injury. Another study published in The Lancet found that the earlier TXA was given, the better the outcomes for patients with TBI.
Administration and Side Effects of Tranexamic Acid
Like all medications, TXA must be administered correctly, and it does come with potential side effects. Generally, TXA is given intravenously (through a vein) in hospital settings. The dose and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the injury and the patient's condition. As for side effects, they can range from mild to severe. Some common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. More serious side effects can include blood clots, allergic reactions, and changes in vision. It's essential for healthcare professionals to monitor patients closely when administering TXA, and patients should always report any side effects they experience.
The Future of Tranexamic Acid in Traumatic Brain Injury Treatment
With the promising results from recent studies, it's clear that TXA has a crucial role to play in the treatment of TBI. However, more research is needed to further refine its use and determine the optimal timing and dosing for different types of injuries. There's also a need for more awareness among healthcare professionals and the public about the benefits of TXA in TBI. As we continue to learn more about this medication and its benefits, I am confident that we will see it being used more effectively and widely in the future.
Chris Rowe
June 28, 2023 AT 22:01Sushmita S
June 30, 2023 AT 21:37AnneMarie Carroll
July 1, 2023 AT 15:17John K
July 3, 2023 AT 14:59Laura Anderson
July 4, 2023 AT 23:02Avis Gilmer-McAlexander
July 6, 2023 AT 20:10Jerry Erot
July 8, 2023 AT 15:14Fay naf
July 8, 2023 AT 18:20ANTHONY SANCHEZ RAMOS
July 10, 2023 AT 13:03Matt Czyzewski
July 11, 2023 AT 07:25John Schmidt
July 12, 2023 AT 10:58Lucinda Harrowell
July 12, 2023 AT 19:25Joe Rahme
July 12, 2023 AT 20:50Leia not 'your worship'
July 14, 2023 AT 16:35Jo Sta
July 15, 2023 AT 16:35KALPESH GANVIR
July 17, 2023 AT 05:19April Barrow
July 18, 2023 AT 23:03Melody Jiang
July 20, 2023 AT 18:28Richa Shukla
July 21, 2023 AT 13:26